Abstract
Despite the remarkable efficacy of novel agents targeting the BTK and BCL2 signaling pathways in CLL, the development of resistance to these drugs has become one of the foremost clinical challenges in the management of CLL patients. An emerging priority is the identification of combinatorial treatments capable of inducing more durable remissions. Recent genomic investigations of CLL have identified altered RNA splicing as a CLL-associated cellular pathway, with heterozygous mutation in the splicing factor SF3B1 representing a common lesion in CLL, associated with transcriptomic alterations in numerous CLL survival pathways. We asked whether alternative splicing was also a more general characteristic of CLL (regardless of SF3B1 status) over normal B cells, and whether changes in alterations generated by a splicing modulator could provide new opportunities for effective combination therapy.
In addressing the first question, we used the tool JuncBASE to quantify the total number of altered splicing events detected in RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data generated from CD19+ B cells collected from 7 normal adult volunteers and 22 patients with CLL (13 SF3B1wt, 9 SF3B1mut). As expected, we detected increased aberrant splicing in SF3B1mut CLLs compared to normal B cells (P=0.02), but also in SF3B1wt CLLs compared to normal B cells (P=0.02), with overall increased splicing alterations in CLL B cells compared to normal B cells (P=0.009). These data suggested that spliceosome modulation could be broadly effective in CLL. Consistent with these findings, we observed increased in vitro loss of viability, per CellTiter Glo luminescence assay, in 20 primary CLLs (10 SF3B1wt, 10 SF3B1mut) to the spliceosome modulator E7107 (E7) across a range of drug concentrations (1nM-1μM).
To define candidate altered splice variants mediating this loss of viability in CLL cells, we performed transcriptome analysis of 11 primary CLL samples exposed to E7 (5nM, 8 hours). The most frequent aberration induced by this drug was intron retention, with >25,000 intron retention events identified after E7 treatment (corrected P -value ≤0.1, |delta PSI|>10, E7 vs. DMSO). Among these, we identified several genes associated with key pathways involved in CLL survival, including BTK, CXCR4, IL4R, CD40, MCL1 and BCL2 .
Since intron-retained transcripts may not be actively translated, we hypothesized that intrinsic dependencies on anti-apoptotic proteins could be modified by E7, and addressed this question by BH3 profiling analysis. We noted consistent increase in BCL2 dependence and decrease in MCL1 dependence upon overnight treatment with E7 (3nM) in 12 CLL samples (P [BCL2]=0.002; P [MCL1]<0.0001) co-cultured with NK-tert stroma, as well as in 4 replicates of CLL splenocytes from Eμ -TCL1 mice (P [BCL2]=0.02; P [MCL1]=0.005), co-cultured with OP9 cells. Together with the RNA-seq findings, these results provided a rational basis for combining E7 with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax.
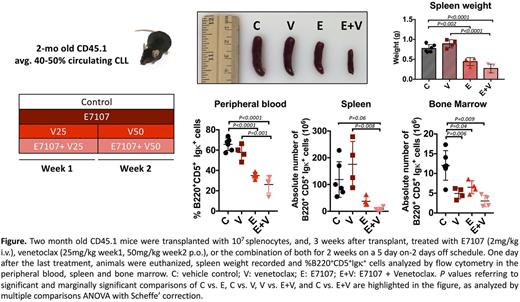
In vitro, treatment with E7 (1nM) and venetoclax (1nM) for 8 hours resulted in increased cytotoxicity across 20 CLLs, with a median viability of 65.9% (34.2- 84.5), compared to 75.9% (58.9-98) and 86.3% (62.9-97.7) after E7 or venetoclax alone, respectively (P <0.0001). Similar results were seen in 6 replicates of CLL splenocytes from Eμ -TCL1 mice (P=0.03). In vivo, in a well-established murine CLL disease model, the Eμ -TCL1 -based adoptive transfer, we observed minimal, if any, sensitivity to venetoclax treatment (dose escalated from 25mg/kg during week 1 to 50mg/kg during week 2) in spleen (SP) and peripheral blood (PB), whereas venetoclax alone was effective in the bone marrow (BM). Two mg/kg E7 was able to reduce leukemia burden in SP, PB and BM, and to overcome venetoclax resistance in SP and PB (Figure). Studies of E7 treatment, alone or combined with venetoclax, for impact on overall survival are ongoing.
In conclusion, we demonstrate that aberrant splicing broadly characterizes CLL lymphocytes, and that spliceosome modulation induces changes in key genes involved in CLL survival across subsets, increasing sensitivity to venetoclax treatment. Combination between E7 and venetoclax showed efficacy in vitro and E7 treatment overcame venetoclax resistance in vivo, providing strong preclinical rationale for testing splicing modulators to improve venetoclax treatment responses in CLL patients.
Valentin: Roche: Other: Travel reimbursement; Abbvie: Other: Travel reimbursement. Seiler: H3 Biomedicine, Inc.: Employment. Smith: H3 Biomedicine Inc.: Employment. Thomas: H3 Biomedicine, Inc.: Employment. Buonamici: H3 Biomedicine, Inc.: Employment. Burger: TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding. Kipps: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Oncternal: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Neuberg: Synta Pharmaceuticals: Other: Stock shares. Davids: Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; InCyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Infinity: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Letai: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Wu: Neon Therapeutics: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal